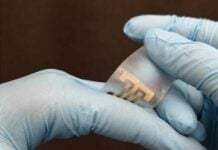
From smartwatches to smart glasses, voice command is being integrated into all sorts of IoT devices. However, these devices do not function properly, especially in noisy environments. Now, a Minneapolis, Minnesota-based wearable device maker is set to launch the world’s smallest EEG device that you can control through your brain waves. The device simply slips over the ear like a headphone and provides users with app- and cloud-based command capabilities, reports Industry Week.
“While this seems to be mind reading, the AI which analyzes the [brain] waves more so is finding a pattern in mental activity associated with a particular category and mapping future waves in the same direction,” says Ian Rowan, the founder and CEO of Nurio. “The Nurio AI engine is not able to ‘decode’ a brain wave into a native language, but rather learns to generalize over patterns in mental activity. This provides pristine data privacy for the users as well.”
Read more CTRL Labs’ Wearable Armband Lets You Control Your Computer with Your Mind
Nurio connects to the Bluetooth on your phone and allows you to track progress just like a smartwatch or fitness tracker. The headphone sized device leverages the latest EEG technology. It uses three dry electrodes and minimal on-device electronics to stream data via Bluetooth to any smart device or computer. This allows for the more powerful processors to leverage the data yielding an energy-efficient, safe and minimal wearable, the Industry Week report said.

Nurio is compatible with other IoT devices. After recording around one minute of thoughts based on that object, nūrio’s AI algorithms can process their future waves into actionable commands. After setting up their device, the user needs to blink twice to trigger the device to begin recording a thought. This is then sent to nūrio servers, which process the raw wave into the user’s device, which ultimately triggers the device.
Read more Controlling Virtual and Augmented Reality with Your Mind
“Our goal was to package EEG electronics into small electronic housing that is comfortable to wear as opposed to some of the larger devices,” says Rowan. “The way we made this possible was to put minimal electronics in the actual device, and instead using a supporting device whether that is a smartphone or computer connected via Bluetooth.”