NovioSense B.V., a Netherlands-based company that develops wireless technology platform for non-invasive monitoring of disease biomarkers, has demonstrated the measurement of tear glucose in diabetic patients and a close correlation to blood glucose with clinically relevant accuracy in a six-patient clinical trial, A second, 24-patient study, to validate the use of the new glucose sensor in type 1 diabetic patients is already under way.
Related Soft Contact Lens Can Monitor Glucose, Medical Conditions and Deliver Drugs
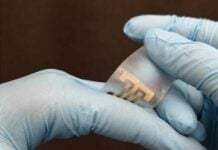
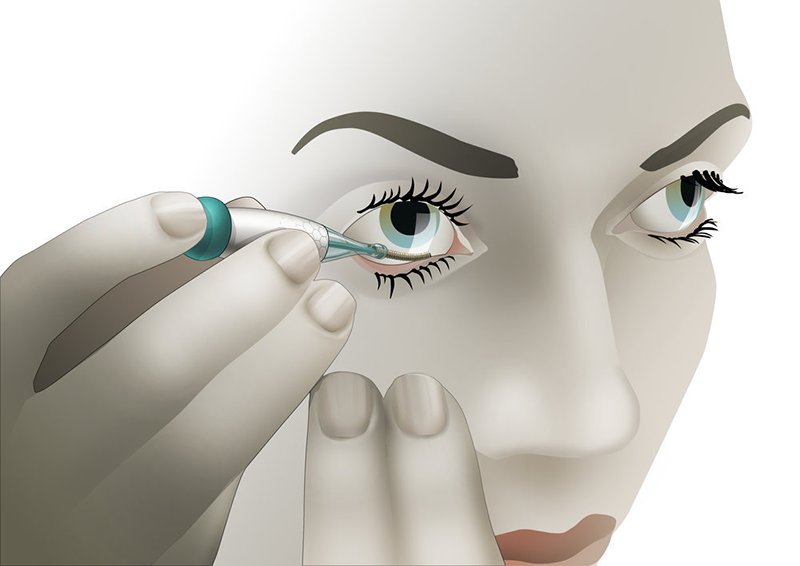
The NovioSense Glucose Sensor is a device that, when placed in the lower eyelid, continuously measures glucose levels in the tear fluid of diabetic patients. The results of the six-patient clinical trial are presented in the American Chemical Society Journal Biomacromolecules.
The completed Phase 2 study was initiated based on positive results from a Phase 1 pilot safety study in 6 healthy subjects. On October 18, 2018 NovioSense initiated a follow-on study in 24 diabetic patients to gather additional evidence for the use of its sensor platform for diabetic patients.
“Today marks an important step in our tear glucose program. We opted to deploy the tear glucose sensor in diabetic patients to obtain evidence that tear glucose levels may be utilized to predict blood glucose levels with a clinically acceptable accuracy,” said Dr. Christopher Wilson, CEO of NovioSense. “These positive results from our phase 2 study demonstrate that the NovioSense Glucose Sensor can be used to measure glucose non-invasively in tears and correlates to blood glucose levels with an accuracy comparable to commercial, minimally invasive devices,” he added.
Linze Dijkstra, Managing Partner of Health Innovations, said they invested in the company in 2012 “based on positive pre-clinical data and are delighted to see year-on-year progress in the development of this disruptive diagnostic platform.”
The flexible miniature sensor developed by NovioSense provides glucose measurements directly to a smartphone when the patient places the device in the lower eyelid.
Related Study Shows MIT’s Non-invasive Blood Glucose Monitor as Accurate as Finger Pricks
The novel eye-wearable is a wireless, battery-free glucose sensor that provides non-invasive, continuous glucose monitoring to people with diabetes at an affordable price. It uses NFC (near-field communication) technology to transfer its readings to a smartphone or another device that can display the measurements and keep a record of them.