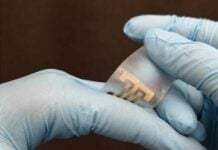
Researchers at Penn State University have developed a new kind of wearable sensor that would deliver real-time medical data to those with eye or mouth diseases, according to Huanyu “Larry” Cheng, Dorothy Quiggle Career Development Professor in the Penn State Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics (ESM).
Read more Penn State Engineers Print Sensors Directly On Human Skin Without Using Heat
Published in Microsystems & Nanoengineering, the small wearable device is designed to be placed near the eyes or mouth to collect data from tears or saliva. Data collected would then be sent to a user’s smartphone or sent to their doctor, reports Mariah Chuprinski in Penn State News.
“We sought to create a device that collects both small and large substances of biofluids such as tears and saliva, which can be analyzed for certain conditions on a rapid, continuous basis, rather than waiting on test results from samples in a lab,” said Cheng, who is also the lead author of the research.
“But a device like this would have to be discreet, soft and comfortable for a patient to agree to wear it,” he said. “And it would have to be a low-cost option for patients.”
The tears- and saliva-sensing technology can help manage diseases like oral ulcers, oral cancer, eye wrinkles, and oral or eye infections like keratitis, which is inflammation of the clear tissue on the front of the eye.

Last year, Cheng published a similar wearable skin patch that collects sweat and tests for pH, sodium, and glucose levels — most helpful for those with hypoglycemia or diabetes.
This new device not only collects data but also administers medicine with a microneedle through the skin around the eye, mouth, or tongue.
“Through nano- to micro-steel ports on the device, we can probe the cell to deliver molecular drugs for treatment in a very efficient process at the cellular level,” Cheng said. “Conversely, the ports can allow us to get access to the gene and coding information on the cell.”
The researchers are developing working prototypes and are in talks with local manufacturers as well as the National Institutes of Health and Amazon for manufacturing the device on a large scale.
“This is a mature technology with a lot of interest behind it,” Cheng said. “There are many possible uses for the device if it makes it to the commercial marketplace.”
With future support from the National Science Foundation, Cheng hopes to extend the technology to other applications as well.