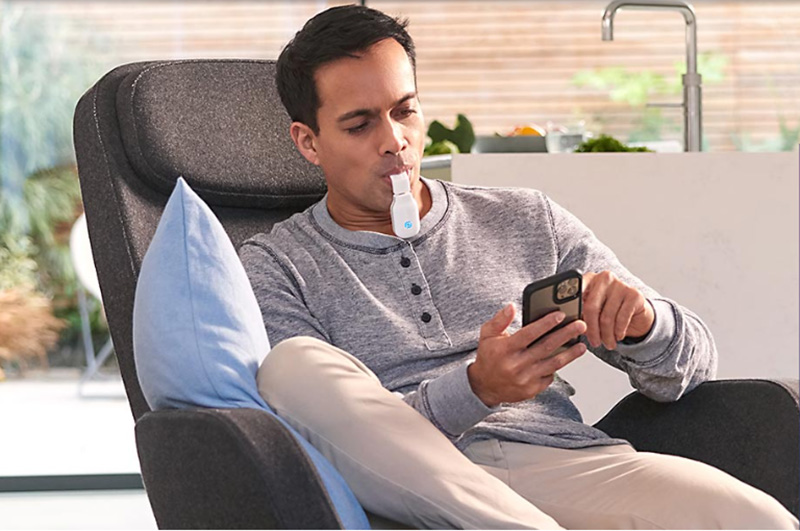
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has authorized marketing of eXciteOSA – a neuromuscular tongue stimulating device that could help prevent sleep apnea and snoring – and it doesn’t need to be worn while sleeping. Signifier Medical Technologies, a company with offices in London and Massachusetts, will market the device.
Read more Onera Bioimpedance Patch Uses Artificial Intelligence to Detect Sleep Apnea
“Obstructive sleep apnea not only impacts sleep quality but can have other serious health impacts if untreated. Today’s authorization offers a new option for the thousands of individuals who experience snoring or mild sleep apnea,” said Malvina Eydelman, MD., director of the Office of Ophthalmic, Anesthesia, Respiratory, ENT and Dental Devices in the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health.
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) occurs when the upper airway becomes blocked repeatedly during sleep, reducing or completely stopping airflow. Untreated OSA can lead to serious complications such as heart attack, glaucoma, diabetes, cancer and cognitive and behavioral disorders.
The eXciteOSA device is the first of its kind cleared by the FDA to treat sleep apnea and snoring by improving tongue muscle function by delivering electrical stimulation to the tongue through a mouthpiece worn for 20 minutes a day. It helps retrain the tongue to prevent it from collapsing backward and blocking airflow during sleep.

Read more Withings Launches New ‘ScanWatch’ with ECG and Sleep Apnea Detection
The FDA assessed the safety and effectiveness of the eXciteOSA device in 115 patients with snoring, including 48 patients with snoring and mild sleep apnea.
Results showed a greater than 20% mean reduction in snoring time (at levels louder than 40dB) in 87 patients, reports FDA. Among patients with mild OSA (n=65), 79% responded to therapy with a mean reduction of 52% in AHI, a 58% reduction in oxygen desaturation index, and a 3.9-point reduction in Epworth Sleepiness Scale score. The most common adverse events observed were excessive salivation, tongue or tooth discomfort, tongue tingling, dental filling sensitivity, metallic taste, gagging, and tight jaw.
The eXciteOSA device is not intended for patients who have or are suspected of having more serious cases of OSA.